広告
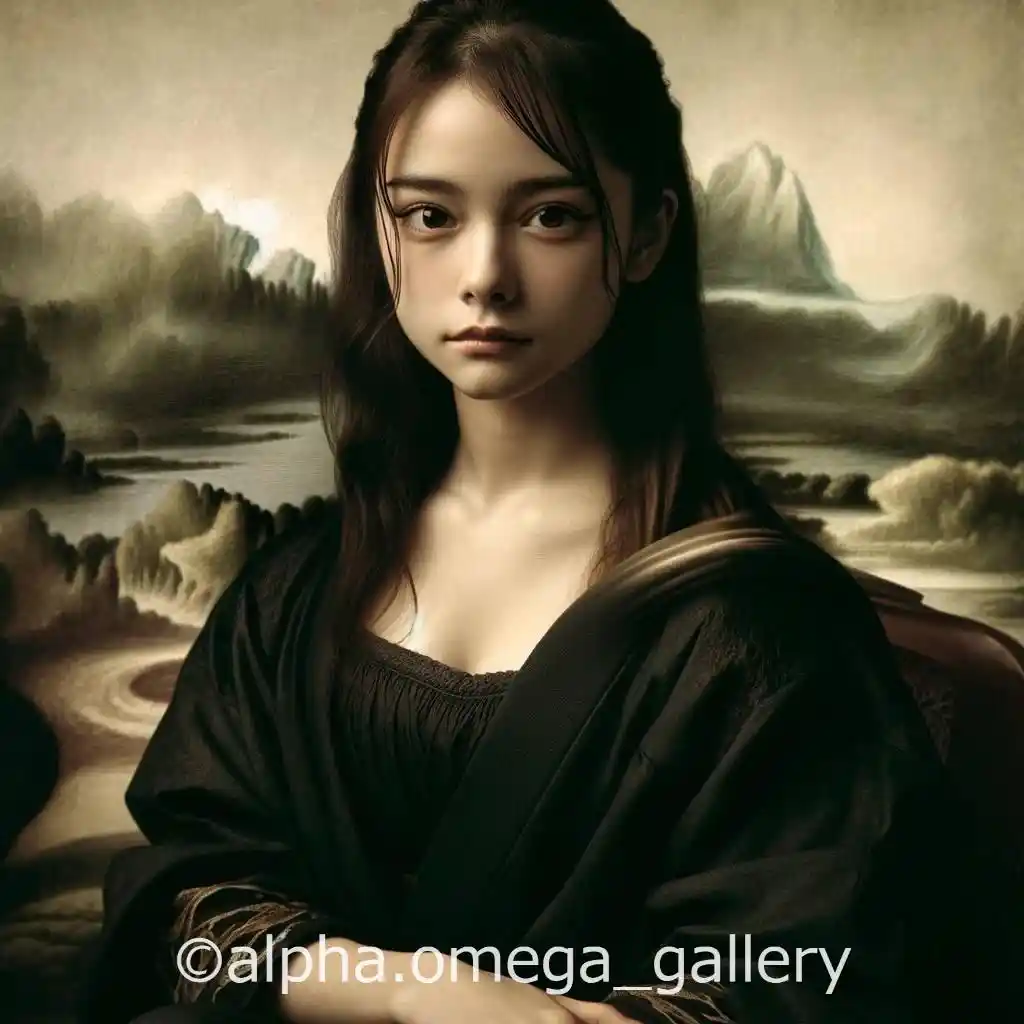

First Impressions of the Reinterpreted Image
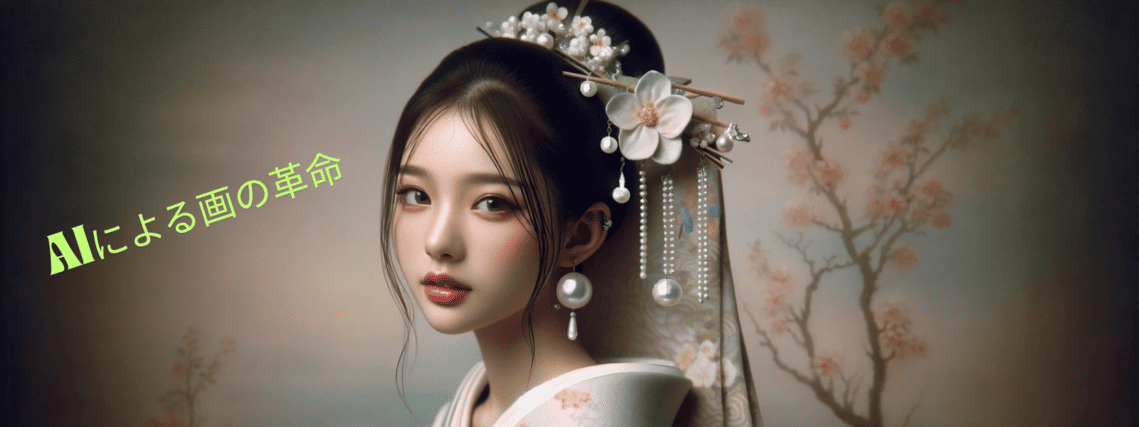
This reinterpreted version of The Mona Lisa is striking. It depicts a woman with features reminiscent of a renowned Japanese actress, highlighting traditional Japanese beauty. While the background and composition recall Leonardo da Vinci’s original masterpiece, this version blends modern artistic elements with a distinct Japanese influence.
Background and History of the Original Masterpiece
Title of the Artwork
Mona Lisa (La Gioconda)
Artist
Leonardo da Vinci
Year of Creation
1503–1506
Historical Context
The Mona Lisa is an iconic portrait from the Italian Renaissance, painted by Leonardo da Vinci. It is believed to depict Lisa Gherardini, the wife of wealthy Florentine merchant Francesco del Giocondo. Renowned for its enigmatic smile, the painting is now housed in the Louvre Museum.
Key Characteristics
The Mona Lisa is famous for its soft expression and mysterious smile. The background features a dreamy, mountainous landscape, characteristic of Leonardo’s painting techniques. He employed the “sfumato” technique, which blurs contours to create a smooth, lifelike transition between light and shadow.
Key Elements of the Reinterpretation
Several aspects of this reinterpretation stand out:
Colour Palette
Like the original painting, this reinterpretation employs a subdued colour scheme. However, the addition of Japanese elements in the background creates a distinctive atmosphere, evoking traditional Japanese landscapes.
Interpretation and Impact of the Reimagined Image
This reimagined piece retains the symbolic essence of The Mona Lisa while incorporating Japanese aesthetics and modern artistic techniques. Featuring a woman resembling a renowned Japanese actress, this artwork offers an Eastern perspective on Leonardo da Vinci’s masterpiece, highlighting both the universality of art and the diversity of beauty standards.